an on-going concern of your dental surgeon

Prosthetic Dentistry
In order to improve the oral-health functions, dental prosthesis is a device to enable the reconstruction or partial replacement of a damaged tooth following decay or dental fracture. It serves as well to replace one or several missing teeth, either with a fixed prothesis (crown, bridge, implant) or with a removable denture, an individual treatment is available for each patient.
Dental prosthesis permit an excellent rehabilitation of the masticatory function, a crucial role in general health. Furthermore they limit the movement of the other teeth and re-establish aesthetic and phonetic functions.
For partial or total tooth loss, the use of dental appliances has the aesthetic advantage to appear identical to natural teeth, it permits a very adequate masticatory function and an elocution improvement.
Dental prosthesis types: either fixed (they are sealed and never come off) or removable, the patient may remove it for cleaning and maintenance.
Fixed denture:

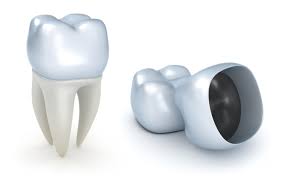
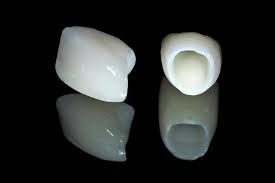
- The crown:
When decay or erosion is far advanced, with or without tooth vitality preservation, the dental surgeon will opt to apply a crown to the damaged tooth in order to protect and restore it. The crown will completely cover the tooth which has been previously prepared to receive the crown, sometimes anchor techniques (inlay, core, richmond…) are used for the crown retention. There are different types of crowns according to medical imperatives and the patient’s budget (all ceramics, metal-ceramics, veneer ceramics or metal)
- The bridge:
a bridge is made up of two or more crowns laid onto the teeth (previously prepared to receive it) on either side of the gap and a false tooth/teeth in between. (These two or more anchoring teeth are called abutment teeth). These false teeth are called pontics and can be made from gold, alloys, porcelain, or a combination of these materials. When possible the nerve of the tooth/teeth supporting the bridge is preserved.
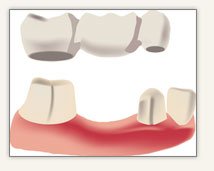
- The main alternative to partial denture is a fixed bridge. Made by putting crowns on the teeth on either side of the space, then joining these two crowns together by placing a false tooth in the space, the bridge is not removable for cleaning for example.
- Another option is an adhesive or "Maryland" bridge. This has wings that are bonded to the back of the supporting teeth with very little drilling involved
- Veneers: a thin covering of the facial surface of a tooth usually constructed of tooth coloured material used to restore discoloured, damaged, misshapen or misaligned teeth. (acting like a false nail on a real nail). It remains the choice technique in anterior teeth aesthetic restoration as it cuts a minima the tooth and preserves the nerve by using a cementing /glueing technique.
- The inlay, onlay: a dental restoration made outside the oral cavity that covers one or more cusp tips and adjoining occlusal surfaces, but not the entire external surface. It is retained by luting cement. When the state of repair or the decay are moderately important but a simple dental treatment is not sufficient, using the inlay or onlay will preserve and restore the tooth. In any case, the patient never remains toothless nor with a ground tooth, a temporary cap is systematically fabricated during the dental care treatment.
Removable dental prosthesis:
Partial dental prosthesis: a prosthetic replacement of one or more missing teeth is chosen when there are sufficient remaining teeth to affix the device to the surrounding teeth. A removable implant prosthesis can be made with either resin (a little bolder and less expensive, it is mostly used as a temporary device) or with a fine and lightweight metal infrastructure called a dental alloy (made with non-precious metal) an economical alternative. It is affixed with brackets onto the chosen abutment teeth or by using clips that are integrated to the appliance.
Fixed denture:
In cases where there are no teeth left, the complete fixed denture is fused directly to the bone, an intimate, in-depth and precise bonding onto the gums.
Implantology’s relevance in modern dental technology: implants may provide a base to various prosthesis and will bring considerable improvement, raise efficiency and comfort in the retention of these prosthetics.
Different types of prosthesis can be integrated on implants.
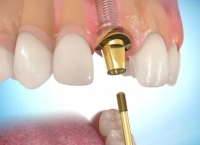
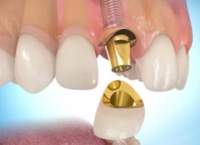
- Fixed implant prosthesis
Connection of the abutment Connection of the crown
- Removable dental prosthesis
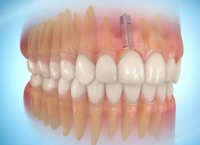
Removable dental prosthesis partial or complete may be fixed using implants. The connection of these removable dentures onto fixed implants takes place under an existing prosthesis or before the implant production.
The removable prosthesis is then attached onto the implant(s) by a fixing device looking like press-studs or by using magnetic attachments thereby avoiding the use of unsightly hooks.
Completion deadline for the construction and fitting of the dental restoration after fixture of the implants: generally an implant must be well integrated to the surrounding bone in which it has been placed (osseointegration) in order to produce and fit the prosthesis (the delay for completion is between two to six months). With the improvements in the production of bone-anchored implants, this delay tends to diminish ; it is however possible immediately after the implant’s positioning, to equip the patient with a provisional denture for reason of convenience, mastication and aesthetics. This interim denture used for the purpose of conditioning the patient to the acceptance of an artificial substitute during the osseointegration period is expressly aesthetic.
OPENING HOURS
Tuesday 09:00 - 18:00
Wednesday 09:00 - 18:00
Thursday 09:00 - 20:00
Friday 08:00 - 16:00
our details to your contacts

Professional web seo content writing and translation services by I. Férigoule-Baker | isabelle.fbaker@gmail.com
 ;
;
 ;
;
 ;
;
 ;
;
 ;
;